JComboBox basic tutorial and examples
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 06 July 2019 | Print Email
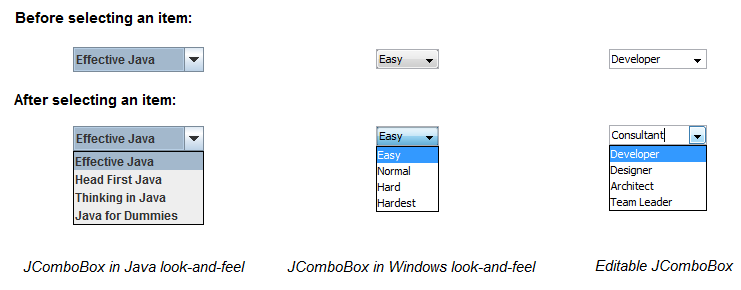 That shows three combo boxes with each in two states:
That shows three combo boxes with each in two states:- Before selecting an item: display of the combo box when there is no action on it (e.g. selecting an item). The combo box is composed of a text and a down-arrow button that lets the user selects an item for the list.
- After selecting an item: display of the combo box when the user is making a selection, a drop-down list of choices is shown up to show available options.
String[] bookTitles = new String[] {"Effective Java", "Head First Java",
"Thinking in Java", "Java for Dummies"};
JComboBox<String> bookList = new JComboBox<>(bookTitles);
// add to the parent container (e.g. a JFrame):
add(bookList);
// get the selected item:
String selectedBook = (String) bookList.getSelectedItem();
System.out.println("You seleted the book: " + selectedBook); That’s for a typical usage of the JComboBox component. Now let’s see other stuffs we can do with this component in details. 1. Creating a new JComboBox component
Basically, we should specify type of the items which the combo box will hold using the generic syntax (the JComboBox class can have parameterized type since Java 7), for example:JComboBox<String> myTitles = new JComboBox<String>(); JComboBox<Integer> myNumbers = new JComboBox<Integer>();
- Creating a default, empty JComboBox then add items later using the addItem()method:
// create an empty combo box with items of type String JComboBox<String> comboLanguage = new JComboBox<String>(); // add items to the combo box comboLanguage.addItem("English"); comboLanguage.addItem("French"); comboLanguage.addItem("Spanish"); comboLanguage.addItem("Japanese"); comboLanguage.addItem("Chinese"); - Creating a JComboBox with an array of items:
// define items in a String array: String[] languages = new String[] {"English", "French", "Spanish", "Japanese", "Chinese"}; // create a combo box with the fixed array: JComboBox<String> comboLanguage = new JComboBox<String>(languages); - Creating a JComboBoxwith a vector of items:
// define items in a vector collection: Vector<String> languages = new Vector<String>(); languages.addElement("English"); languages.addElement("French"); languages.addElement("Spanish"); languages.addElement("Japanese"); languages.addElement("Chinese"); // create a combo box with the given vector JComboBox<String> comboLanguage = new JComboBox<String>(languages); - Creating a JComboBox with items of a custom type:
Generally a combo box can hold items of any type. If the type of the items is a custom object other than String, then the object’s toString() method will be used to get name of the items in the drop-down list. Following is an example that creates a combo box with items of a custom type Job:
JComboBox<Job> jobList = new JComboBox<Job>();
jobList.addItem(new Job("Developer"));
jobList.addItem(new Job("Designer"));
jobList.addItem(new Job("Architect"));
jobList.addItem(new Job("Team Leader")); The class Job is defined as follows:
class Job {
private String jobTitle;
public Job(String jobTitle) {
this.jobTitle = jobTitle;
}
public String toString() {
return this.jobTitle;
}
}Keep in mind that we have to override the toString() method to return a textual representation of the Job class, so the JComboBox class can use it to show item’s name in the drop-down list. 2. Creating an editable combo box
By default, a JComboBox component is created in read-only mode, which means the user can only pick one item from the fixed options in the drop-down list. What if we want to allow the user to provide his own option besides the fixed ones? Well, in this case we can simply use the setEditable() method to make the combo box editable:// code to create a combo box as above... // make it editable myComboBox.setEditable(true);The following screenshot shows how an editable combo box looks like:
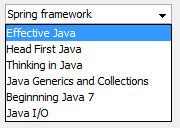 As we can see, the user can type “Spring framework” into the combo box as the drop-down list does not contain that title.
As we can see, the user can type “Spring framework” into the combo box as the drop-down list does not contain that title. 3. Using a custom ComboBoxModel
Besides using an array or a vector as items for the combo box (in this case, the JComboBox will create a default model), it’s also possible to use a custom data model in order to have more control over the items (especially for items of a custom type). To create a custom model class for the combo box, create a class that implements the interface ComboBoxModel and override the interface’s methods. However we don’t need to implement the ComboBoxModel interface directly, as Swing provides a default implementation class called DefaultComboBoxModel which already does the basic stuffs. Here’s an example of a custom model class for combo box:class MyComboBoxModel extends DefaultComboBoxModel<Job> {
public MyComboBoxModel(Job[] items) {
super(items);
}
@Override
public Job getSelectedItem() {
Job selectedJob = (Job) super.getSelectedItem();
// do something with this job before returning...
return selectedJob;
}
}This custom model class, MyComboBoxModel extends the DefaultComboBoxModel class for the custom type Job, and overrides its getSelectedItem() method to control how a selected item would be returned. And we can pass an instance of this model class when creating a new JComboBox object as follows:Job[] jobs = new Job[] {
new Job("Developer"), new Job("Designer"), new Job("Tester")
};
MyComboBoxModel myModel = new MyComboBoxModel(jobs);
JComboBox<Job> jobList = new JComboBox<Job>(myModel);Or we can set the custom model for the combo box after it’s created like this:JComboBox<Job> jobList = new JComboBox<Job>(); jobList.setModel(myModel);
4. Adding the combo box to a container
After created, the combo box should be added to a container like a JFrame or JPanel which can have different layout managers. For example:- Adding the combo box to a JFrame with FlowLayout manager:
theFrame.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); theFrame.add(myComboBox);
- Adding the combo box to a JPanel with BorderLayout manager:
thePanel.add(myComboBox, BorderLayout.CENTER);
- Adding the combo box to a JPanel with GridBagLayout manager:
thePanel.setLayout(new GridBagLayout()); GridBagConstraints constraints = new GridBagConstraints(); // set constraints details... constraints.gridx = 1; thePanel.add(myComboBox, constraints);
5. Working with items in the combo box
The common operations we can do with items in the combo box are adding, removing, setting selected item, getting selected item, and getting total number of items. Here are some examples:- Adding new items to the combo box (using the addItem()method):
String[] bookTitles = new String[] {"Effective Java", "Head First Java", "Thinking in Java"}; JComboBox<String> bookList = new JComboBox<String>(bookTitles); // add more books bookList.addItem("Java Generics and Collections"); bookList.addItem("Beginnning Java 7"); bookList.addItem("Java I/O"); - Adding new items if using a custom model (using the addElement() method of the DefaultComboBoxModel class) :
Job[] jobs = new Job[] {new Job("Developer"), new Job("Designer"), new Job("Tester")}; MyComboBoxModel myModel = new MyComboBoxModel(jobs); myModel.addElement(new Job("Consultant")); myModel.addElement(new Job("Manager")); JComboBox<Job> jobList = new JComboBox<Job>(myModel);Note that the addItem() method of the JComboBox class still works in case of using a custom model. - Removing items from the combo box (using the removeItem() or removeItemAt()methods):
// remove an item of type String bookList.removeItem("Thinking in Java"); // remove an item of a custom type Job // the Job class must override the equals() method Job consultantJob = new Job("Consultant"); jobList.removeItem(consultantJob); // remove an item at a given index: jobList.removeItemAt(2); - Removing all items (using the removeAllItems()method):
bookList.removeAllItems();
- Setting selected item (using the setSelectedItem() or setSelectedIndex()methods):
// set selected item of type String: bookList.setSelectedItem("Head First Java"); // set selected item of a custom type Job: // the Job class must override the equals() method Job consultantJob = new Job("Consultant"); jobList.setSelectedItem(consultantJob); // set selected item at a given index: jobList.setSelectedIndex(1); - Getting selected item (using the getSelectedItem() or getSelectedIndex()methods):
// get the selected item as an object String selectedBook = (String) bookList.getSelectedItem(); Job selectedJob = (Job) jobList.getSelectedItem(); // get the selected item as an index: int selectedIndex = jobList.getSelectedIndex();
- Getting an item at a specified index (using the getItemAt()method):
// get the 4th item in the list String item4th = bookList.getItemAt(3);
- Getting total number of items in the combo box (using the getItemCount() method):
// get total number of items: int totalBooks = bookList.getItemCount();
6. Adding an event listener
Basically we can handle the event that happens when the user is selecting an item from the combo box’s drop-down list. Here’s an example:bookList.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
JComboBox<String> combo = (JComboBox<String>) event.getSource();
String selectedBook = (String) combo.getSelectedItem();
if (selectedBook.equals("Effective Java")) {
System.out.println("Good choice!");
} else if (selectedBook.equals("Head First Java")) {
System.out.println("Nice pick, too!");
}
}
});The ActionEvent will be fired whenever an item is selected from the drop-down list, and perhaps this is the only useful action which we’re interested when working with JComboBox. 7. Customizing combo box’s appearance
There are few things we can do to change the combo box’s default appearance out-of-the-box such as changing font style, font color for the selected item’s text:bookList.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
bookList.setFont(new Font("Arial", Font.BOLD, 14)); And limit the maximum number of items displayed in the drop-down list:bookList.setMaximumRowCount(5);In this case, if the combo box contains more than 5 items, then the drop-down list will show only the first 5 ones and add a vertical scroll bar to navigating the rest items. This would be useful if we have a combo box with many items, thus such limitation is needed.Here’s the screenshot of a combo box whose appearance is customized as above:
 See the tutorial Create custom GUI for JComboBox If you want to have a custom combo box looks like this:
See the tutorial Create custom GUI for JComboBox If you want to have a custom combo box looks like this:
8. A Swing demo program for JComboBox
For your reference, we created a small Swing program to demo the usage of the JComboBox component. The program looks like this: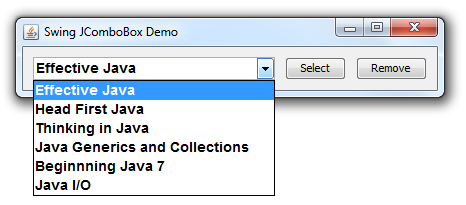 It contains an editable combo box and two buttons. You can type new title into the combo box and hit Enter, and the new title will be added to the drop-down list. On clicking the Select button, a message dialog appears saying what is the selected book:
It contains an editable combo box and two buttons. You can type new title into the combo box and hit Enter, and the new title will be added to the drop-down list. On clicking the Select button, a message dialog appears saying what is the selected book: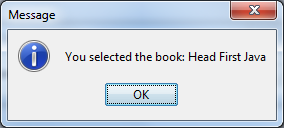 On clicking the Remove button, the currently selected item will be removed from the combo box. You can download full source code as well as executable JAR file of this program under the attachments section.
On clicking the Remove button, the currently selected item will be removed from the combo box. You can download full source code as well as executable JAR file of this program under the attachments section.Related JCombBox Tutotrials:
Other Java Swing Tutorials:
- Java Swing Hello World Tutorial for Beginners Using Text Editor
- JFrame basic tutorial and examples
- JPanel basic tutorial and examples
- JLabel basic tutorial and examples
- JTextField basic tutorial and examples
- JCheckBox basic tutorial and examples
- JList basic tutorial and examples
- JTree basic tutorial and examples
- A Simple JTable Example for Display
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.