- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 04 July 2019 | Print Email
In this tutorial, we demonstrate how to use
JComboBox as an editor for cells in a
JTable component. We will end up creating the following Swing program:
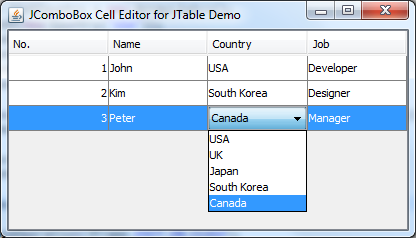
Look, when editing a cell in the column Country, a dropdown list (implemented by a
JComboBox component) is displayed and allows the user to pick an available item from the list. This creates convenience experience for the user. Let’s see how to code such a program.The program consists of the following classes:
- JComboBoxTableCellEditorExample: this is the main Swing program that displays a list of persons in tabular format (using JTable component) with some dummy data. Each row in the table represents a person whose country can be changed by editing the corresponding cell in the Country column.
- Person: this is the POJO class that represents a person.
- PersonTableModel: this is the model class for the JTable.
- Country: a POJO class represents a country which is an attribute of a person.
- CountryCellRenderer: A cell renderer class for the Country column.
- CountryCellEditor: A cell editor class for the Country column.
The Person class:
package net.codejava.swing.jtable.editor.combobox;
/**
* A model class that represents a person.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class Person {
private String name;
private Country country;
private String job;
public Person(String name, Country country, String job) {
this.name = name;
this.country = country;
this.job = job;
}
// getters and setters...
}Notice that the attribute country of the
Person class is of type
Country whose code is as below.
The Country class:
package net.codejava.swing.jtable.editor.combobox;
/**
* A model class represents a country.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class Country {
private String name;
public Country(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
} The PersonTableModel class:
package net.codejava.swing.jtable.editor.combobox;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.swing.table.AbstractTableModel;
/**
* A custom table model for the table of persons.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class PersonTableModel extends AbstractTableModel {
private String[] columnNames = {"No.", "Name", "Country", "Job"};
private List<Person> listPerson = new ArrayList<>();
public PersonTableModel(List<Person> listPerson) {
this.listPerson.addAll(listPerson);
}
@Override
public int getColumnCount() {
return columnNames.length;
}
public String getColumnName(int column) {
return columnNames[column];
}
public Class getColumnClass(int column) {
return getValueAt(0, column).getClass();
}
@Override
public int getRowCount() {
return listPerson.size();
}
@Override
public void setValueAt(Object value, int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
Person person = listPerson.get(rowIndex);
switch (columnIndex) {
case 1:
person.setName((String) value);
break;
case 2:
person.setCountry((Country) value);
break;
case 3:
person.setJob((String) value);
break;
}
}
@Override
public Object getValueAt(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
Object returnValue = null;
Person person = listPerson.get(rowIndex);
switch (columnIndex) {
case 0:
returnValue = rowIndex + 1;
break;
case 1:
returnValue = person.getName();
break;
case 2:
returnValue = person.getCountry();
break;
case 3:
returnValue = person.getJob();
break;
}
return returnValue;
}
public boolean isCellEditable(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
return columnIndex > 0;
}
}This table model class is very important, as it defines how the
JTable displays the model data (a list of persons) to the view (the table) and how the
JTable converts the user-edited data back to the model data. Notice the following methods must be overridden from the
AbstractTable class:
- getColumnClass(...): returns class type for each column in the table. The JTable will bind cell renderers and cell editors based on return values from this method.
- setValueAt(…): tells the JTable how to map user-edited values with model data. In this case, it sets user-edited values to corresponding attributes of the Person class.
- getValueAt(...): tells the JTable how to map model data to its view. In this case, it returns the attributes of Person class corresponding to rowIndex and columnIndex.
- isCellEditable(...): determines which cell can be edited. In this case, all cells from the second column toward can be edited.
The CountryCellRenderer class:
package net.codejava.swing.jtable.editor.combobox;
import java.awt.Component;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.table.DefaultTableCellRenderer;
/**
* A custom renderer for cells in the Country column.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class CountryCellRenderer extends DefaultTableCellRenderer {
public Component getTableCellRendererComponent(JTable table, Object value,
boolean isSelected, boolean hasFocus, int row, int column) {
if (value instanceof Country) {
Country country = (Country) value;
setText(country.getName());
}
if (isSelected) {
setBackground(table.getSelectionBackground());
} else {
setBackground(table.getSelectionForeground());
}
return this;
}
}This is a very simple renderer which is actually a
JLabel (the
DefaultTableCellRenderer class extends
JLabel class). It simply displays name of country of a person.
The CountryCellEditor class:
package net.codejava.swing.jtable.editor.combobox;
import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.List;
import javax.swing.AbstractCellEditor;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.table.TableCellEditor;
/**
* A custom editor for cells in the Country column.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class CountryCellEditor extends AbstractCellEditor
implements TableCellEditor, ActionListener {
private Country country;
private List<Country> listCountry;
public CountryCellEditor(List<Country> listCountry) {
this.listCountry = listCountry;
}
@Override
public Object getCellEditorValue() {
return this.country;
}
@Override
public Component getTableCellEditorComponent(JTable table, Object value,
boolean isSelected, int row, int column) {
if (value instanceof Country) {
this.country = (Country) value;
}
JComboBox<Country> comboCountry = new JComboBox<Country>();
for (Country aCountry : listCountry) {
comboCountry.addItem(aCountry);
}
comboCountry.setSelectedItem(country);
comboCountry.addActionListener(this);
if (isSelected) {
comboCountry.setBackground(table.getSelectionBackground());
} else {
comboCountry.setBackground(table.getSelectionForeground());
}
return comboCountry;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
JComboBox<Country> comboCountry = (JComboBox<Country>) event.getSource();
this.country = (Country) comboCountry.getSelectedItem();
}
}This is the interesting cell editor that returns a
JComboBox component each time the user edits a cell in the Country column. A list of Country objects is passed into its constructor in order to add countries to the dropdown list. Then, the selected item is set to the country of the current person. When the user chooses another country from the list, the selected country will be set as return value of the editor. In turn, the
JTable updates the selected country to the current person (through the
getCellEditorValue() method of the editor, and the
setValueAt() method of the
PersonTableModel class). Notice that we should add action listener for the combo box.In both the renderer and editor, we use the following code snippet:
if (isSelected) {
comboCountry.setBackground(table.getSelectionBackground());
} else {
comboCountry.setBackground(table.getSelectionForeground());
}That set background color of the renderer/editor according to selection state of the table row, so that the customized cell doesn’t look ‘different’ when its row is selected.
The main Swing program
Here’s full source code of the main program:
package net.codejava.swing.jtable.editor.combobox;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
/**
* This Swing program demonstrates the technique of customizing JTable's
* cell editor using a JComboBox.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class JComboBoxTableCellEditorExample extends JFrame {
private JTable table = new JTable();
private PersonTableModel tableModel;
public JComboBoxTableCellEditorExample() {
super("JComboBox Cell Editor for JTable Demo");
List<Person> listPerson = new ArrayList<>();
listPerson.add(new Person("John", new Country("USA"), "Developer"));
listPerson.add(new Person("Kim", new Country("South Korea"), "Designer"));
listPerson.add(new Person("Peter", new Country("UK"), "Manager"));
List<Country> listCountry = new ArrayList<>();
listCountry.add(new Country("USA"));
listCountry.add(new Country("UK"));
listCountry.add(new Country("Japan"));
listCountry.add(new Country("South Korea"));
listCountry.add(new Country("Canada"));
tableModel = new PersonTableModel(listPerson);
table.setModel(tableModel);
table.setDefaultRenderer(Country.class, new CountryCellRenderer());
table.setDefaultEditor(Country.class, new CountryCellEditor(listCountry));
table.setRowHeight(25);
JScrollPane scrollpane = new JScrollPane(table);
scrollpane.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(400, 200));
add(scrollpane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
pack();
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
new JComboBoxTableCellEditorExample();
}
});
}
}Notice the code snippet that sets model, renderer and editor for the table:
tableModel = new PersonTableModel(listPerson);
table.setModel(tableModel);
table.setDefaultRenderer(Country.class, new CountryCellRenderer());
table.setDefaultEditor(Country.class, new CountryCellEditor(listCountry));
You can download full source code and executable JAR file of the demo program in the attachments section.
API References:
Related JTable Tutorials:
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He started programming with Java in the time of Java 1.4 and has been falling in love with Java since then. Make friend with him on
Facebook and watch
his Java videos you YouTube.
 Look, when editing a cell in the column Country, a dropdown list (implemented by a JComboBox component) is displayed and allows the user to pick an available item from the list. This creates convenience experience for the user. Let’s see how to code such a program.The program consists of the following classes:
Look, when editing a cell in the column Country, a dropdown list (implemented by a JComboBox component) is displayed and allows the user to pick an available item from the list. This creates convenience experience for the user. Let’s see how to code such a program.The program consists of the following classes: Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He started programming with Java in the time of Java 1.4 and has been falling in love with Java since then. Make friend with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos you YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He started programming with Java in the time of Java 1.4 and has been falling in love with Java since then. Make friend with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos you YouTube.