How to display images from database in JSP page with Java Servlet
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 04 July 2019 | Print Email
- Retrieve the image data from the database as an array of bytes, by using JDBC. If you are using Hibernate, this can be done transparently by the framework.
- Encode the image’s binary data to String representation in Base64 format.
- Display the image on a JSP page using <IMG> tag with image source is the base64 string.
1. The Database
Suppose that we have a table named book that has a column called image which is of type LONGBLOB (this type can store files up to 4GB):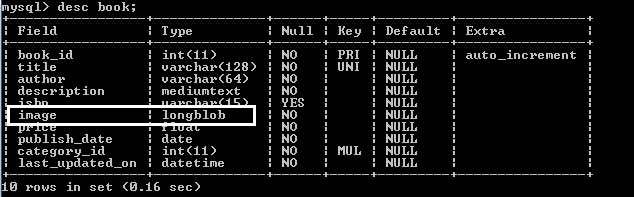 So our ultimate goal is to retrieve image data from this column and display the image on a web page.
So our ultimate goal is to retrieve image data from this column and display the image on a web page.
2. The Java Model Class
The Java model class for the table needs to have a field to store the base64 string representation of the image. For example:package net.codejava;
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
private String base64Image;
public String getBase64Image() {
return base64Image;
}
public void setBase64Image(String base64Image) {
this.base64Image = base64Image;
}
// other fields...
// other getters and setters…
}The field’s setter setBase64Image() will be called by a DAO class that retrieves the image binary data and converts it to a base64 string.The field’s getter getBase64Image() will be called by a JSTL tag in the JSP page in order to show the image.package net.codejava;
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
private byte[] image;
@Column(name = "image")
public byte[] getImage() {
return this.image;
}
private String base64Image;
public String getBase64Image() {
return base64Image;
}
public void setBase64Image(String base64Image) {
this.base64Image = base64Image;
}
// other fields...
// other getters and setters
} 3. The DAO Class
In the DAO class, we write some additional code for retrieving the image’s binary data and converting it to a base64 string. Given a ResultSet object named result, the following code reads the image column into a byte array, and then converts it to a String in base64 format:Blob blob = result.getBlob("image");
InputStream inputStream = blob.getBinaryStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int bytesRead = -1;
while ((bytesRead = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
byte[] imageBytes = outputStream.toByteArray();
String base64Image = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(imageBytes);
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();The Base64 class can be found in the java.util package.In case Hibernate is used, simply update the getter getBase64Image() as follows:@Transient
public String getBase64Image() {
base64Image = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(this.image);
return base64Image;
}And the following is sample code of a DAO class - BookDAO:package net.codejava;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Blob;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Base64;
public class BookDAO {
String databaseURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bookstoredb";
String user = "root";
String password = "pass";
public Book get(int id) throws SQLException, IOException {
Book book = null;
String sql = "SELECT * FROM book WHERE book_id = ?";
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(databaseURL, user, password)) {
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, id);
ResultSet result = statement.executeQuery();
if (result.next()) {
book = new Book();
String title = result.getString("title");
String author = result.getString("author");
Blob blob = result.getBlob("image");
InputStream inputStream = blob.getBinaryStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int bytesRead = -1;
while ((bytesRead = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
byte[] imageBytes = outputStream.toByteArray();
String base64Image = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(imageBytes);
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
book.setTitle(title);
book.setAuthor(author);
book.setBase64Image(base64Image);
}
} catch (SQLException | IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
throw ex;
}
return book;
}
}As you can see, the get(int id) method finds a row in the book table that associates with the specified id. If the row is found, a new Book object is created and populated its information like this:book.setTitle(title); book.setAuthor(author); book.setBase64Image(base64Image);
4. The Servlet Class
In the Servlet class, it receives request from the user with the specified book ID, then it calls the DAO to retrieve the Book object, which is then stored as a request attribute. Finally the servlet forwards the processing to a destination JSP page.Here is sample code of the servlet class:package net.codejava;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/viewbook")
public class GetBookServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public GetBookServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
int bookId = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id"));
BookDAO dao = new BookDAO();
try {
Book book = dao.get(bookId);
request.setAttribute("book", book);
String page = "/index.jsp";
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(page);
requestDispatcher.forward(request, response);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new ServletException(ex);
}
}
} 5. Display Image in the JSP Page
To display the image represented by a base64 String, use the <IMG> tag with the following syntax:<img src="data:image/jpg;base64,[base_64_String_goes_here]" />
And here is code of a sample JSP page that uses JSTL tags mixed with HTML tags:<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<html>
<body>
<div align="center">
<h2><c:out value="${book.title}" /></h2>
<h3><c:out value="${book.author}" /></h3>
<img src="data:image/jpg;base64,${book.base64Image}" width="240" height="300"/>
</div>
</body>
</html> 6. Test Image Display
Suppose that the book table contains some rows with image data. To test if the image gets displayed in the JSP page or not, call the Java Servlet by typing the following URL in a web browser:http://localhost:8080/Bookshop/viewbook?id=1
You can see the book image gets displayed as shown in the following screenshot: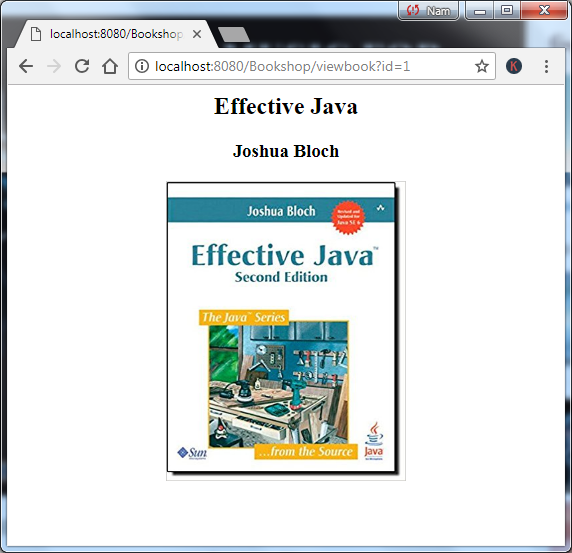 So far you have learned how to implement a solution that helps display images from database in JSP page, without having to store images somewhere on the server’s disk. The key point here is using the <IMG> tag with a base64 String that represents the image.
So far you have learned how to implement a solution that helps display images from database in JSP page, without having to store images somewhere on the server’s disk. The key point here is using the <IMG> tag with a base64 String that represents the image. Other Java Coding Tutorials:
- How to implement forgot password feature for Java web application
- How to implement remember password (remember me) for Java web application
- How to code login and logout with Java Servlet, JSP and MySQL
- How to Code Hit Counter for Java web application
- 10 Common Mistakes Every Beginner Java Programmer Makes
- 10 Java Core Best Practices Every Java Programmer Should Know
- How to become a good programmer? 13 tasks you should practice now
- How to calculate MD5 and SHA hash values in Java
- Java File Encryption and Decryption Example
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.